VDI vs RDS: Key Differences & How to Choose the Right Remote Access Solution
When a business wants to provide remote access to desktops and applications, two major technologies usually appear in the conversation:
- VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure)
- RDS (Remote Desktop Services)
Both allow employees to work remotely — but they work very differently.
Understanding the Core Concepts
What Is VDI?
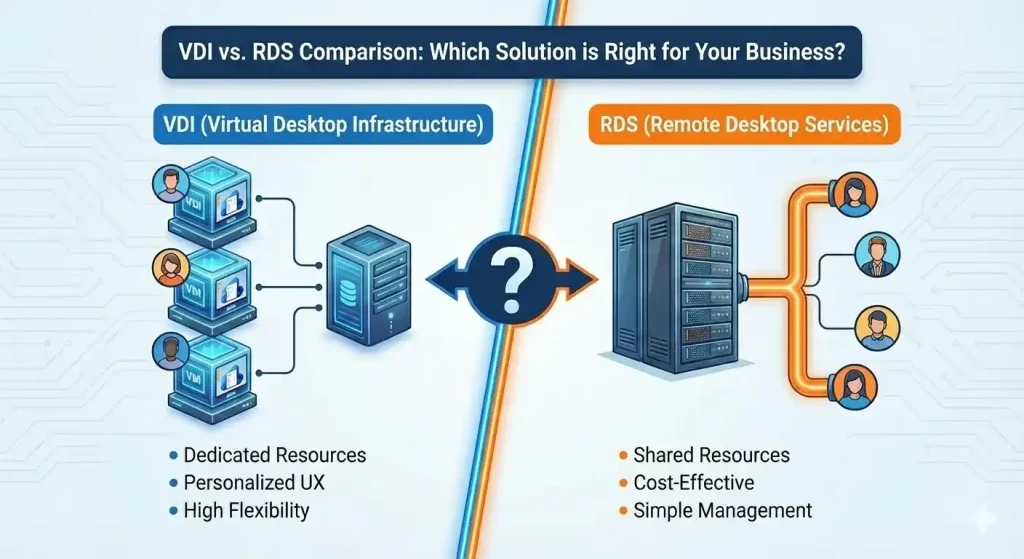
VDI delivers full virtual desktops, each running its own operating system.
Every user gets their own isolated virtual machine.
What Is RDS?
RDS provides shared sessions on a Windows Server.
Multiple users use the same OS instance at the same time.
VDI vs RDS: The Main Differences
1. User Experience
- VDI: Feels like a personal PC
- RDS: More like a shared environment
2. Cost
- VDI: More expensive (requires more hardware)
- RDS: Very cost-effective for large teams
3. Performance
- VDI: Best for heavy workloads, graphics apps, or personalized setups
- RDS: Excellent for Office work, CRM, ERP, accounting apps
4. Scalability
- VDI: Scalable but requires more resources
- RDS: Scales quickly and cheaply
5. Use Cases
VDI is ideal for:
- Developers
- Designers
- Technical users who need custom environments
RDS is perfect for:
- Call centers
- Administrative teams
- Offices running shared applications
So Which One Is Right for You?
The answer depends on your needs:
Choose VDI if:
✔ Your users need personalized desktops
✔ You run heavy graphical or engineering apps
✔ Security isolation is a major concern
Choose RDS if:
✔ You want fast, affordable remote access
✔ Most employees use the same applications
✔ You need a simple, scalable solution
Many organizations actually combine both for maximum flexibility.
